 In the complex realm of payment card systems, where transactions zip seamlessly across borders and through digital channels, a seemingly innocuous string of digits plays a pivotal role: the Issuer Identification Number (IIN). Often overlooked by the casual user, these numbers form the backbone of card payment infrastructure, quietly ensuring that transactions are authorized, routed, and secured with precision. This article aims to decode the multifaceted role of Issuer Identification Numbers (IINs) within payment card systems, shedding light on their significance and impact.
In the complex realm of payment card systems, where transactions zip seamlessly across borders and through digital channels, a seemingly innocuous string of digits plays a pivotal role: the Issuer Identification Number (IIN). Often overlooked by the casual user, these numbers form the backbone of card payment infrastructure, quietly ensuring that transactions are authorized, routed, and secured with precision. This article aims to decode the multifaceted role of Issuer Identification Numbers (IINs) within payment card systems, shedding light on their significance and impact.
At first glance, an IIN might appear as just the initial digits of a card number. However, beneath this apparent simplicity lies a wealth of information crucial for the functioning of the entire payment ecosystem. An IIN serves as a unique identifier, indicating the institution that issued the card and providing essential details about its type and network affiliation. Whether it’s a credit, debit, prepaid, or another form of payment card, the IIN acts as a digital fingerprint, guiding transactions through a labyrinth of networks and systems.
Understanding the intricacies of IINs is not merely an academic exercise; it’s essential for anyone involved in payment processing, from financial institutions to merchants and consumers. For financial institutions, accurate IIN management is fundamental for efficient card issuance, fraud prevention, and compliance with industry regulations. Merchants rely on IIN data to facilitate smooth transactions and mitigate risks associated with fraudulent activity. Even consumers, though unaware, benefit from the security measures enabled by robust IIN protocols, safeguarding their financial transactions from unauthorized access and misuse.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the anatomy of Issuer Identification Numbers, exploring how they are structured, utilized, and evolving to meet the demands of an ever-evolving payment landscape. Through this exploration, a clearer understanding of the indispensable role played by IINs in payment card systems will emerge, illuminating the intricate mechanisms that underpin the modern economy.
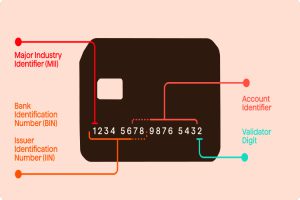
Structure and Composition of Issuer Identification Numbers (IINs)
- Numeric Range and Length:IINs typically consist of the first six digits of a payment card number. These digits are carefully assigned by international standards bodies such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the American National Standards Institute (ANSI). The length and range of IINs are designed to accommodate the vast array of financial institutions worldwide while maintaining uniqueness and integrity.
- Issuer Identification:The first few digits of an IIN signify the issuing institution, providing valuable information about the card issuer. This information includes the bank or financial organization’s identity, country of origin, and sometimes even specific details such as the type of card (credit, debit, prepaid) and the card network (Visa, Mastercard, American Express, etc.). Understanding this structure allows for swift identification of card origins and streamlines transaction processing.
- Industry Standards and Regulations:The assignment and management of IINs are governed by industry standards and regulatory frameworks to ensure consistency, security, and interoperability across the payment ecosystem. Organizations like the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council (PCI SSC) play a crucial role in establishing and maintaining these standards, fostering trust and reliability in payment card systems globally.
Role of Issuer Identification Numbers in Transaction Processing
- Transaction Authorization:
IINs play a pivotal role in transaction authorization by providing essential information about the card issuer and card type. When a transaction occurs, the merchant’s point-of-sale system or online payment gateway uses the IIN to identify the card issuer and route the transaction through the appropriate networks for approval. This process ensures that transactions are authorized efficiently and securely.
- Fraud Detection and Prevention:
IINs are instrumental in fraud detection and prevention strategies employed by financial institutions and payment processors. By analyzing patterns and anomalies in IIN data, fraud detection systems can identify suspicious transactions and flag them for further review. Additionally, IIN-based rules and algorithms help prevent fraudulent activities such as card cloning and unauthorized card usage, safeguarding both consumers and financial institutions from potential losses.
- Compliance and Reporting:
Issuer Identification Numbers also play a crucial role in compliance and reporting requirements imposed by regulatory bodies and card networks. Financial institutions and payment service providers must accurately report and track transaction data associated with specific IINs to ensure compliance with regulations such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) and the Dodd-Frank Act. Proper management and documentation of IIN-related information are essential for maintaining regulatory compliance and avoiding penalties or sanctions.
Evolution of Issuer Identification Numbers in the Digital Age
With the rapid evolution of payment technologies and the proliferation of digital transactions, the role of Issuer Identification Numbers (IINs) has undergone significant transformations. Traditional card-based payments are now complemented by a diverse array of digital payment methods, including mobile wallets, contactless payments, and peer-to-peer transfers. Consequently, the scope and application of IINs have expanded to encompass these emerging payment modalities, requiring adaptations to existing standards and infrastructure. For instance, while traditional IIN structures primarily catered to physical card transactions, modern IIN frameworks must accommodate the unique identifiers associated with digital payment tokens and virtual cards, ensuring seamless interoperability and security across digital channels.
Conclusion:
The intricate role of Issuer Identification Numbers (IINs) in payment card systems emerges as a cornerstone of modern financial infrastructure. From their humble origins as mere numerical sequences, IINs have evolved into indispensable tools driving the efficiency, security, and interoperability of global payment ecosystems. Through the lens of this exploration, it becomes evident that IINs are not merely digits but rather linchpins connecting financial institutions, merchants, and consumers in a web of trust and reliability.
Looking ahead, the journey of IINs continues to unfold, propelled by the forces of technological innovation, regulatory change, and shifting consumer expectations. As we embrace the future, it is essential to recognize the enduring importance of IINs as pillars of trust and security in an increasingly digital world. By fostering collaboration, driving innovation, and upholding the principles of integrity and transparency, we can harness the full potential of Issuer Identification Numbers to shape a more inclusive, efficient, and resilient financial ecosystem for generations to come. In doing so, we honor the legacy of IINs as guardians of trust and enablers of progress in the ever-evolving landscape of payment card systems.
Disclaimer: “This article is for educational & entertainment purposes.”
