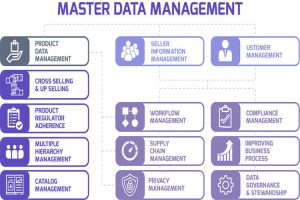
 In today’s dynamic digital landscape, safeguarding organizational assets and sensitive data is paramount. As cyber threats evolve in sophistication and frequency, businesses must adopt robust measures to fortify their defenses. Enter Security Master Data Management (SMDM), a strategic approach that amalgamates data management principles with security protocols to enhance organizational protection comprehensively.
In today’s dynamic digital landscape, safeguarding organizational assets and sensitive data is paramount. As cyber threats evolve in sophistication and frequency, businesses must adopt robust measures to fortify their defenses. Enter Security Master Data Management (SMDM), a strategic approach that amalgamates data management principles with security protocols to enhance organizational protection comprehensively.
At its core, SMDM focuses on centralizing, standardizing, and managing security-related data across an organization. By establishing a unified repository for critical security information, such as user credentials, access controls, and encryption keys, SMDM empowers businesses to streamline security operations, minimize vulnerabilities, and respond swiftly to emerging threats.
Through meticulous data governance practices, SMDM ensures the accuracy, integrity, and confidentiality of security data, thereby instilling trust and confidence in organizational processes. By orchestrating seamless integration with existing security technologies and frameworks, such as Identity and Access Management (IAM) and Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems, SMDM fosters a cohesive security ecosystem capable of adapting to evolving risk landscapes.
Moreover, SMDM facilitates proactive risk mitigation by enabling real-time monitoring, analysis, and reporting of security metrics and anomalies. This proactive stance empowers organizations to preempt potential breaches and maintain regulatory compliance effortlessly.
In essence, SMDM serves as a linchpin in fortifying organizational resilience against cyber threats, offering a holistic and adaptive approach to security management that is indispensable in today’s digital age.
How Security master data management works
Security Master Data Management (SMDM) operates through a systematic approach that integrates data management principles with security protocols to fortify organizational defenses. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how SMDM works:
- Data Identification and Classification: The process begins with identifying and classifying security-related data assets within the organization. This includes sensitive information such as user credentials, access logs, encryption keys, and security policies.
- Centralized Repository Establishment: SMDM establishes a centralized repository or database to store and manage security master data. This repository serves as a single source of truth for all security-related information, ensuring consistency and accuracy across the organization.
- Data Standardization: Standardization of security data is crucial for ensuring uniformity and interoperability. SMDM applies data standardization techniques to harmonize formats, naming conventions, and metadata across different types of security data.
- Data Governance Implementation: Robust data governance practices are implemented to govern the security master data throughout its lifecycle. This involves defining roles and responsibilities, enforcing access controls, and establishing policies for data quality, privacy, and security.
- Integration with Security Technologies: SMDM seamlessly integrates with existing security technologies and frameworks deployed within the organization, such as Identity and Access Management (IAM), Security Information and Event Management (SIEM), and Threat Intelligence platforms. This integration ensures interoperability and enables unified security operations.
- Automated Data Management Processes: Automation plays a key role in SMDM by streamlining data management processes such as data ingestion, validation, cleansing, and synchronization. Automated workflows and scripts are used to perform routine tasks, reducing manual effort and human error.
- Real-time Monitoring and Analysis: SMDM enables real-time monitoring and analysis of security master data to detect anomalies, identify security incidents, and assess risks. This involves implementing monitoring tools, generating alerts, and conducting continuous assessments of data integrity and compliance.
- Incident Response and Remediation: In the event of a security incident or breach, SMDM facilitates rapid incident response and remediation by providing timely access to relevant security data and insights. Incident response playbooks and automated workflows are leveraged to contain and mitigate the impact of security incidents.
- Continuous Improvement and Adaptation: SMDM follows a continuous improvement approach by regularly evaluating and updating security master data management processes, policies, and technologies. This ensures that the organization remains resilient to emerging threats and regulatory requirements.
- Compliance and Reporting: SMDM supports compliance efforts by maintaining audit trails, generating compliance reports, and facilitating regulatory assessments. This helps demonstrate adherence to industry standards and regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX.
By following these steps, Security Master Data Management (SMDM) helps organizations establish a robust foundation for protecting sensitive data and mitigating cyber security risks effectively.
The Protecting of sensitive data to mitigate cyber Attack
Protecting sensitive data is essential to mitigate cybersecurity risks effectively. This process involves several key steps:
- Data Classification: Identify and classify sensitive data based on its level of confidentiality, integrity, and availability requirements.
- Access Controls: Implement robust access controls to restrict unauthorized access to sensitive data. This includes role-based access control (RBAC), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and least privilege principles.
- Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data both in transit and at rest to prevent unauthorized interception or access. Strong encryption algorithms and key management practices are crucial in this regard.
- Data Masking or Anonymization: Mask or anonymize sensitive data in non-production environments to reduce the risk of exposure during development, testing, or analytics processes.
- Monitoring and Auditing: Deploy monitoring tools and techniques to track access to sensitive data, detect suspicious activities, and generate audit logs for forensic analysis and compliance reporting.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Implement DLP solutions to prevent the unauthorized transmission or exfiltration of sensitive data outside the organization’s network perimeter.
- Employee Training and Awareness: Educate employees about the importance of protecting sensitive data through cybersecurity training programs and awareness campaigns. Encourage best practices such as strong password management and vigilant phishing detection.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and regularly update an incident response plan to effectively respond to and mitigate the impact of data breaches or cybersecurity incidents involving sensitive data.
By implementing these measures, organizations can significantly reduce the likelihood and impact of cyber attacks aimed at compromising sensitive data, thus enhancing their overall cyber security posture.
Conclusion
In conclusion, safeguarding sensitive data is paramount in mitigating cyber security risks. Through proactive measures such as data classification, access controls, encryption, and continuous monitoring, organizations can fortify their defenses against cyber threats. By prioritizing employee training and incident response preparedness, they can effectively detect, contain, and mitigate security breaches. Ultimately, a robust data protection strategy not only helps maintain regulatory compliance but also preserves trust with stakeholders and safeguards the integrity and reputation of the organization in an increasingly digital world.
Disclaimer: “This article is for educational & entertainment purposes.”
