 In the fast-paced world of global finance, precision and clarity are paramount. Amidst the vast array of investment opportunities spanning continents, the International Securities Identification Number (ISIN) stands as a beacon of standardization and uniformity. Designed to facilitate seamless identification and tracking of securities across international markets, the ISIN plays a pivotal role in modern finance.
In the fast-paced world of global finance, precision and clarity are paramount. Amidst the vast array of investment opportunities spanning continents, the International Securities Identification Number (ISIN) stands as a beacon of standardization and uniformity. Designed to facilitate seamless identification and tracking of securities across international markets, the ISIN plays a pivotal role in modern finance.
An ISIN is a unique, alphanumeric code assigned to a specific security, serving as its distinct identifier in the financial markets. Much like a fingerprint for financial instruments, the ISIN encapsulates vital information about the security, including its issuer, type, and characteristics. With its standardized format, consisting of 12 characters, the ISIN transcends geographical boundaries, enabling investors and market participants to efficiently access and trade a diverse array of securities.
The genesis of the ISIN can be traced back to the need for a unified system to streamline the identification and trading of securities on a global scale. Recognizing the challenges posed by disparate national systems, financial authorities, and market participants collaborated to establish the ISIN as a universal identifier, fostering transparency and efficiency in the capital markets.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into everything you need to know about ISIN, exploring its significance, structure, and practical applications in the world of finance. From its inception to its current role as a cornerstone of securities trading, we illuminate the critical role that ISIN plays in facilitating investment activities worldwide. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or a newcomer to the financial markets, understanding the intricacies of ISIN is essential for navigating the complexities of modern finance with confidence and precision.
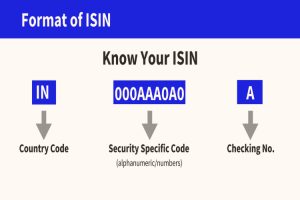
The Structure and Components of ISIN
- Alphanumeric Composition:An ISIN typically consists of a 12-character code, comprising letters and numbers. This alphanumeric structure ensures uniqueness and facilitates easy identification of securities.
- Country Code:The first two characters of the ISIN represent the country or region of the security issuer. These codes are assigned according to the ISO 6166 standard, ensuring consistency across borders.
- Security Identifier:Following the country code, the next nine characters constitute the specific identifier for the security. This segment distinguishes one security from another within the same jurisdiction.
- Check Digit:The final character of the ISIN serves as a check digit, calculated using a formula to verify the integrity of the code. This digit helps detect errors or inconsistencies in the ISIN, enhancing its reliability as a unique identifier.
The Role and Importance of ISIN in Global Finance
- Facilitating Cross-Border Trading:
ISINs play a crucial role in enabling the seamless trading of securities across international markets. By providing a standardized identifier, ISINs simplify the process of buying and selling securities across different jurisdictions, reducing administrative burdens and facilitating liquidity.
- Enhancing Transparency and Market Efficiency:
ISINs contribute to greater transparency and efficiency in the financial markets by ensuring accurate identification and tracking of securities. Investors can easily access essential information about security using its ISIN, such as its issuer, type, and trading status, enabling informed decision-making and risk management.
- Regulatory Compliance:
Regulatory authorities worldwide mandate the use of ISINs for reporting and compliance purposes. By requiring securities to be identified with ISINs, regulators can monitor market activity, detect potential abuses, and enforce regulatory requirements effectively.
- Supporting Risk Management and Investor Protection:
ISINs are integral to risk management and investor protection efforts. By providing a standardized means of identifying securities, ISINs enable investors to assess and manage risks more effectively, ensuring the integrity and stability of the financial system.
- Facilitating Market Data Management:
ISINs are widely used in market data management systems to organize and categorize information about securities. Financial institutions and data vendors rely on ISINs to ensure accuracy and consistency in their databases, enabling efficient data retrieval and analysis.
The Process of ISIN Assignment and Maintenance
The assignment and maintenance of ISINs involve a systematic process to ensure accuracy and reliability. Financial institutions, such as stock exchanges, regulatory bodies, or national numbering agencies, are typically responsible for issuing ISINs. When a new security is created, its issuer submits relevant details to the designated authority, including information about the security’s characteristics and issuer details. Based on this information, the authority assigns a unique ISIN to the security, following established standards and guidelines.
Once assigned, ISINs require ongoing maintenance to reflect any changes or updates to the security. This includes actions such as corporate actions (e.g., mergers, acquisitions, stock splits) or changes in the security’s terms and conditions. Market participants must ensure that ISINs are accurately updated to reflect these changes, thereby preserving the integrity and reliability of the identifier. Failure to maintain accurate ISIN records can lead to confusion, errors, and potential compliance issues in the financial markets.
Efficient maintenance of ISINs involves robust data management systems and collaboration among various stakeholders. Financial institutions and market participants rely on secure databases and automated processes to track and update ISIN information promptly. Regular audits and compliance checks help ensure the accuracy and completeness of ISIN records, mitigating risks associated with outdated or incorrect data.
Conclusion:
In the ever-evolving landscape of global finance, understanding the International Securities Identification Number (ISIN) is paramount for investors, regulators, and market participants alike. As a standardized identifier for securities, the ISIN serves as a cornerstone of transparency, efficiency, and reliability in the modern financial markets.
From its structured composition to its role in facilitating cross-border trading and enhancing market transparency, the significance of ISIN cannot be overstated. Through its unique alphanumeric code, the ISIN enables seamless identification and tracking of securities across international markets, fostering liquidity and accessibility for investors worldwide.
Moreover, the process of ISIN assignment and maintenance underscores the importance of accuracy and diligence in preserving the integrity of securities identification systems. By adhering to established standards and guidelines, financial institutions and market participants ensure the reliability and trustworthiness of ISIN records, thereby mitigating risks and upholding market integrity.
Looking ahead, the evolution of ISIN and its integration with technological advancements offer promising opportunities to enhance efficiency and transparency in the financial markets. As blockchain technology and digital asset management systems continue to gain traction, ISINs may play an increasingly vital role in facilitating real-time tracking and verification of securities transactions.
Disclaimer: “This article is for educational & entertainment purposes.”
